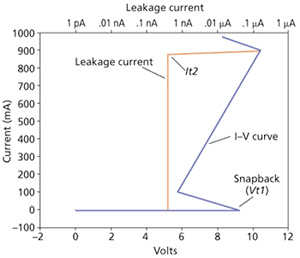
傳輸線脈衝(TLP,Transmission Line Pulse)測試,屬於半導體產品靜電放電的先期模擬方法。TLP透過每次使用一個脈衝條件,已獲得一個I-V點的方式,持續的施加下,直到漏電(leakage)超過規格值為止。
TLP測試過程中經常會有snapback的現象。snapback的保護裝置在Vt1有一個t1觸發點。在ESD瞬間放電能量持續地進入保護裝置時會使得保護裝置的特性曲線進入snapback區域。ESD瞬間放電能量再持續地進入保護裝置時亦會使得保護裝置的特性曲線形成一個低阻抗放電路徑用來排出ESD瞬間放電的能量。當電壓與電流持續上升到It2,此為晶片可承受最大電流,又稱為二次擊穿點,晶片將無法恢復原本的特性。
華證科技ESD實驗室,擁有完整的服務種類,目前使用的設備包括了ThermoFisher的MK2、MK4、Orion2、Orion3,目前也引進了日本新一代的Hanwa ESD測試機台。除台灣新竹外,在上海金橋, 安徽合肥均有服務機台,可提供客戶快速的驗證服務。此外,在安徽合肥更配置了TLP,可以協助研發人員在第一時間驗證晶片ESD保護設計的完整性,協助客戶產品快速進入市場。
 傳輸線脈衝(TLP,Transmission Line Pulse)測試,屬於半導體產品靜電放電的先期模擬方法。TLP透過每次使用一個脈衝條件,已獲得一個I-V點的方式,持續的施加下,直到漏電(leakage)超過規格值為止。
傳輸線脈衝(TLP,Transmission Line Pulse)測試,屬於半導體產品靜電放電的先期模擬方法。TLP透過每次使用一個脈衝條件,已獲得一個I-V點的方式,持續的施加下,直到漏電(leakage)超過規格值為止。